Oh differentiation – a word that strikes fear, frustration, and angst into the hearts of teachers everywhere. So often we are told to differentiate our guided math instruction by going “deeper not wider”. When we ask “What does that look like? Give me a specific example.”…we are told more word problems. YOU ALL. As a teacher who has been there, I understand how frustrating this is. Over the next few weeks, we’re going to take a look at ways to deepen, differentiate, and level our instruction in ways that don’t involve (1) moving on to another grade level’s standards, (2) burying our students in word problems or (3) providing supplemental enrichment activities/worksheets.
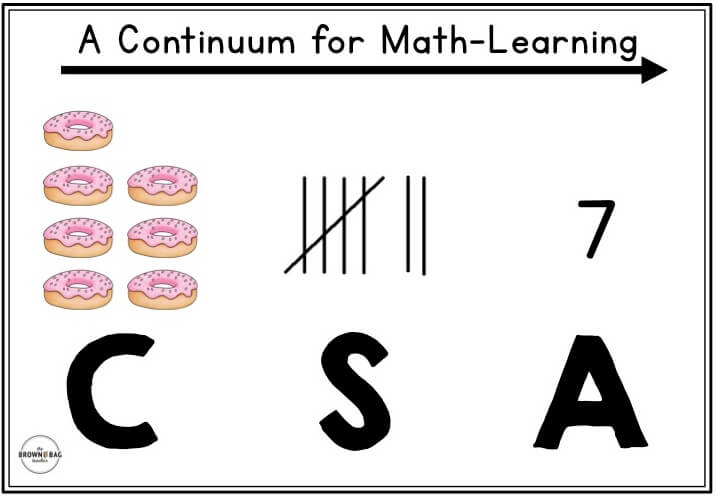
Today we’re going to explore the continuum along which mathematicians construct their understanding of numbers – CSA (concrete, semi-concrete, abstract). Understanding this progression as a teacher allows us to assess where students are and intentionally scaffold them to develop their math thinking.
What is CSA?
Previously called CPA (concrete, pictorial, abstract) and CRA (concrete, representational, abstract), CSA (concrete, semi-concrete, abstract) is a continuum in which mathematical knowledge is constructed. It is not always linear and many times the stages overlap and/or need to be revisited.
Working with this continuum, rather than against it allows students to understand mathematical concepts before learning the “rules” or procedures of math. Offering a context for the numbers, as well as, individual interpretations of numbers, makes math meaningful.
How Can I Use CSA to Differentiate?
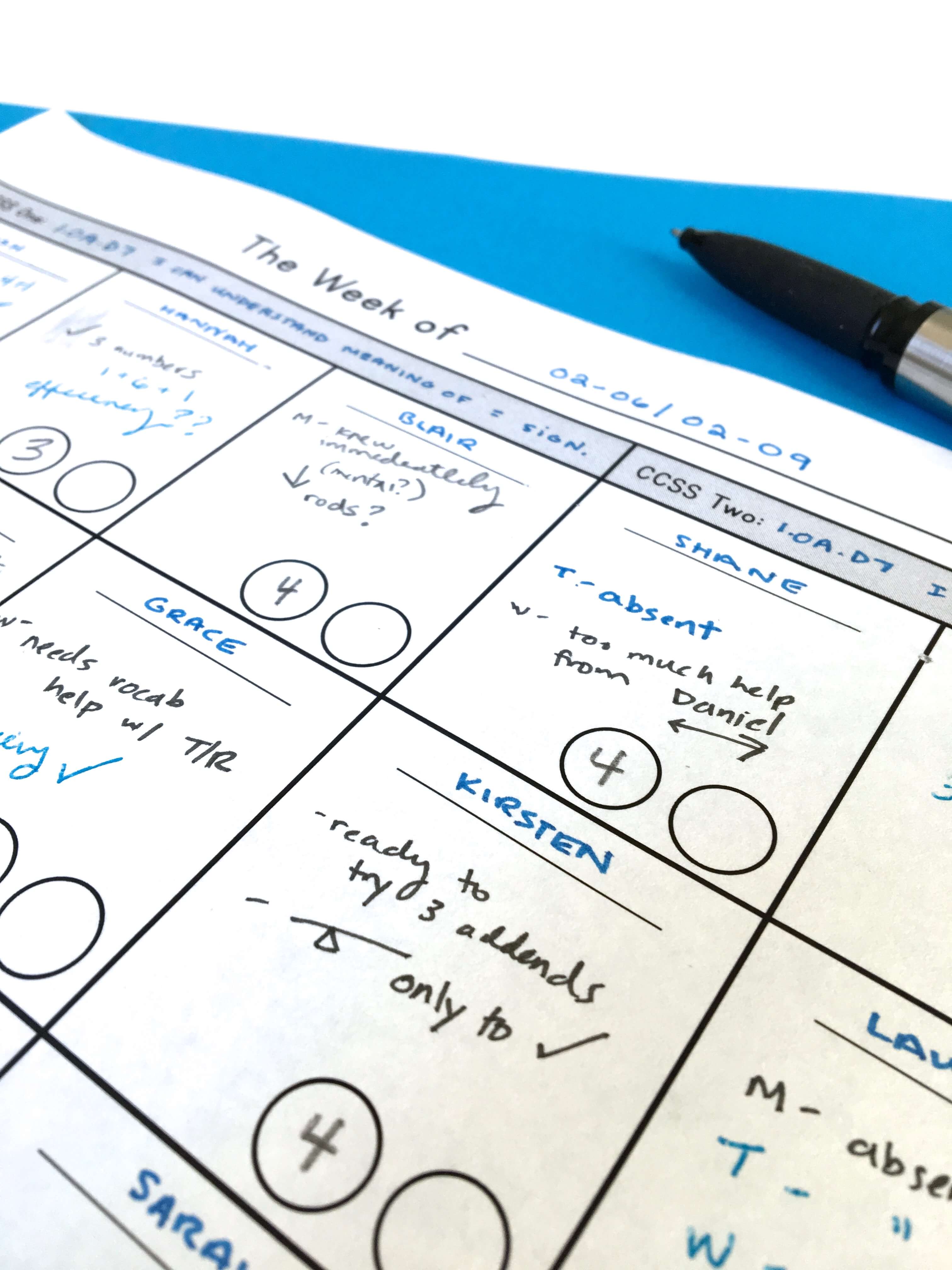
The power of a Guided Math structure is found in teacher observations. We, as teachers, should be carefully observing student behavior as they engage during small-group time. Are students holding numbers in their heads and counting on or are they backing up and getting a running start when counting? Does a student instantly recognize 7 on the ten frame, recognize 5 and count on two more, or individual count the counters 1-7? These careful observations allow you to flexibly group students, provide more/less support, and challenge student thinking. Working within the continuum of CSA, I know that my students who are struggling with one-to-one counting need LOTS of concrete experiences with numbers with many different manipulatives, whereas students with a solid understanding of quantity may be ready to use the more abstract number balance to represent number quantity. Rather than planning 3 different Guided Math lessons each day, I am teaching the same 1st Grade Common Core Standards just at the just-right place along the CSA continuum. This may mean the manipulatives each group is using are different, that one group is branching into illustrations (in addition to the concrete manipulatives) or I am asking students to branch into the abstract. As a teacher, I am intentionally making instructional decisions of when to push, support, or reframe, based on what I see. Snag this FREE log here.
Working in the Concrete
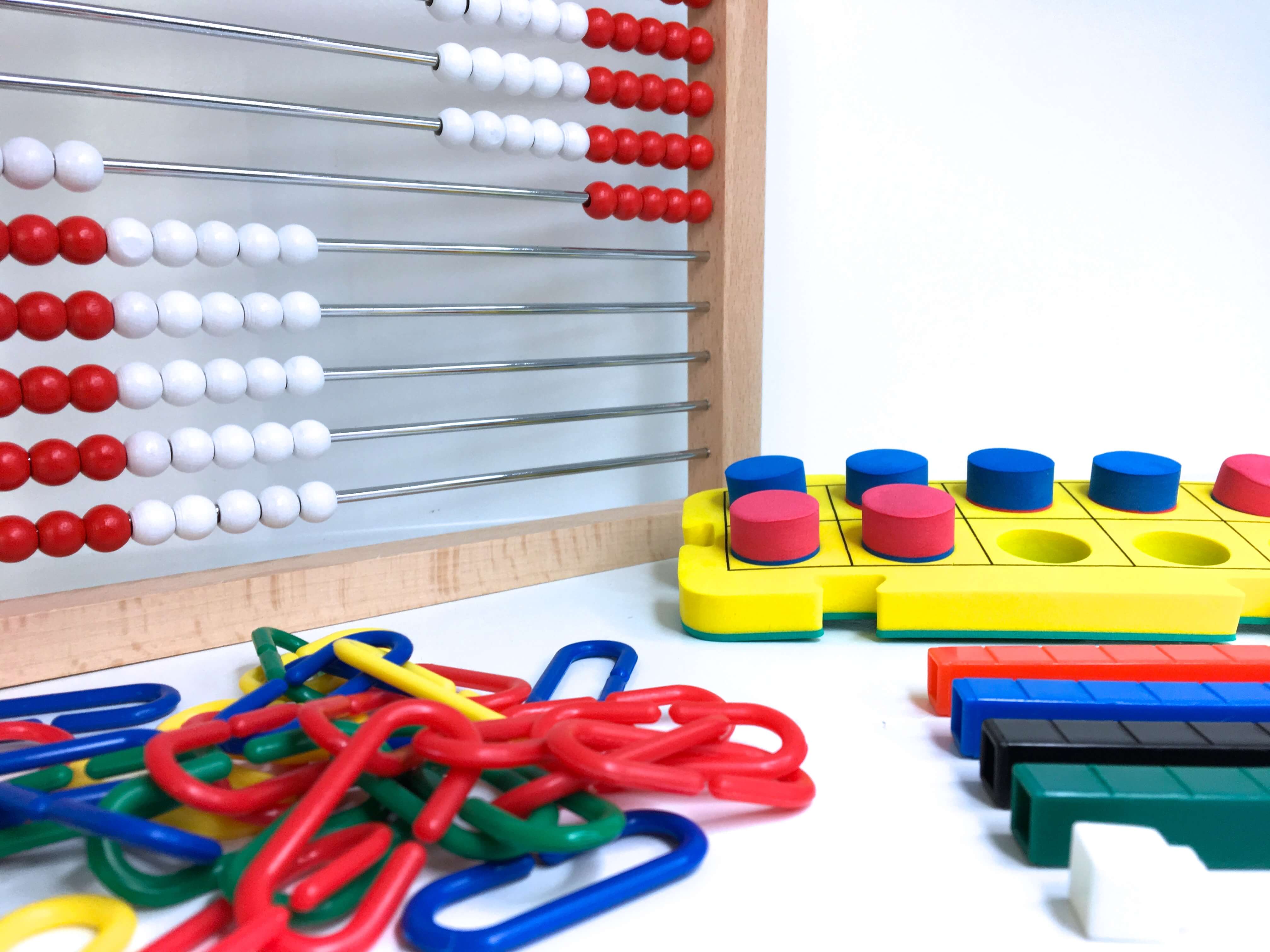
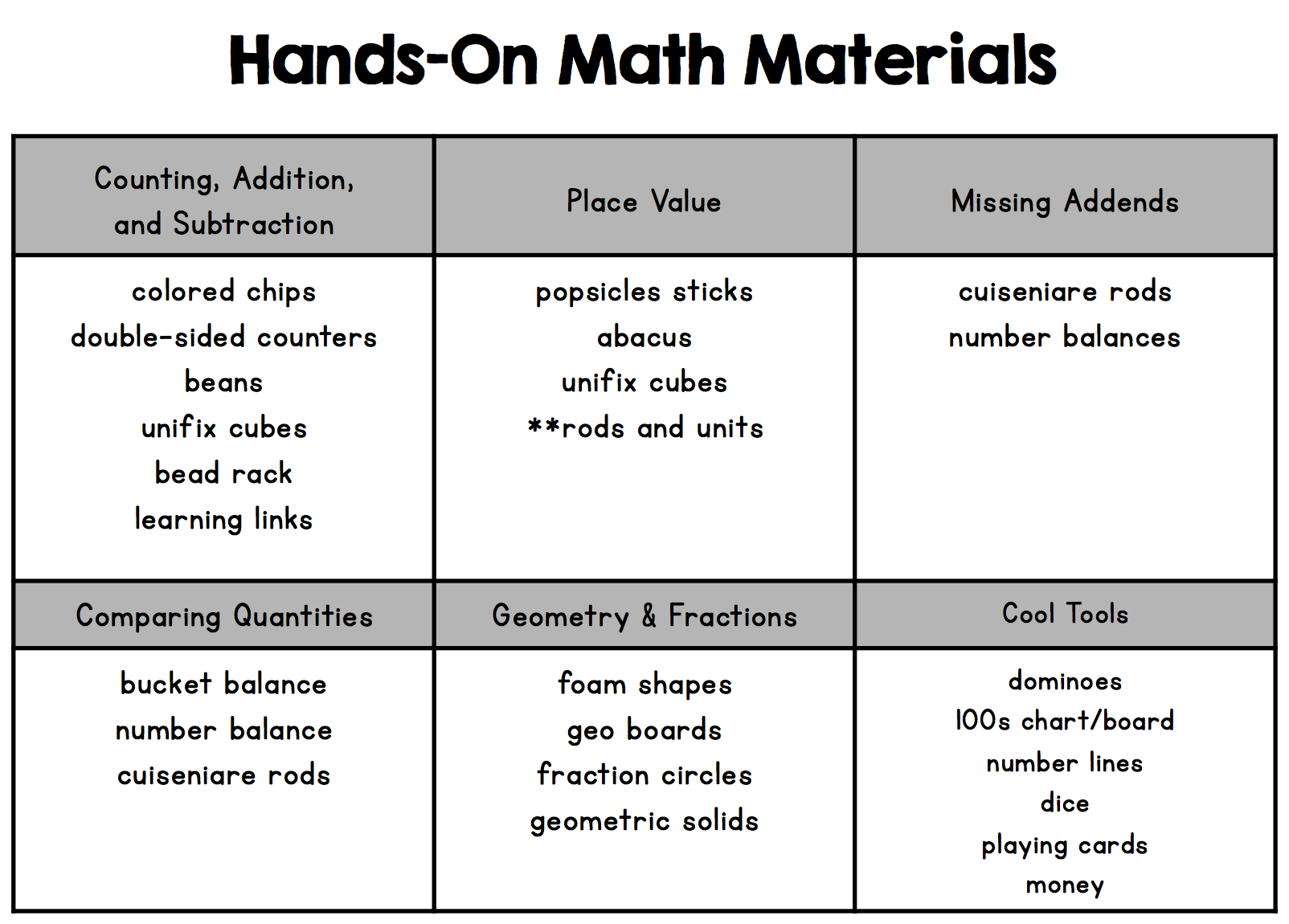
In the concrete stage of learning, students are given hands-on opportunities to explore and build numbers. At this stage students are using hands-on manipulatives to represent their thinking. A teacher might record student thinking with an illustration or model but students are jumping to using numbers to share their thinking because they aren’t ready yet. It is during this concrete stage that we want lots of different manipulatives for students to use – bead racks, double-sided counters, cuisenaire rods, bucket balances, abaci, etc. At this point we are avoiding math tools that don’t have inherent value (i.e. coins, number lines, 100s charts, place value rods)
A significant portion of Common Core Standards for Kindergarten, 1st Grade, and 2nd grade show mastery with concrete objects in play. Meaning that students can reach “mastery” using base ten pieces, counters, or bead racks. These manipulatives aren’t a crutch; rather, they are considered developmentally appropriate as students build conceptual (true) understanding of math concepts. Gradually these supports are intentionally pulled and replaced with different ways of representing numbers (drawings, illustrations, numbers, etc).
Working in the Semi-Concrete
Working in the semi-concrete, students are using illustrations and drawings to represent math concepts. These drawings might include circles, x’s, drawing the base 10 pieces, tally markers, etc. As students begin creating these illustrations, we don’t abandon concrete manipulatives; rather, use them in conjunction with one another.
Initially a semi-concrete representation might be quite literal. For example, a student using drawings of flowers to represent flowers in the word problem. I see this most often in my kindergarten mathematicians. While we often see this behavior as “time-killing” initially, it is actually developmentally-appropriate depending on the depth of mastery. As students become a little more abstract in their semi-concrete thinking, these drawings will become a little less literal (i.e. drawing circles to represent the flowers).
Not all students will spend a lot of time in the semi-concrete stage of mathematical development, but representations and illustrations often become a more efficient (i.e. faster) and easily accessible (i.e. I don’t always carry double-sided counters in my pocket) way to work-out math thinking.
Working in the Abstract
Then, with some of the math standards with some students, we bridge into abstract experiences with numbers. Since numbers have no inherent value without a concrete representation, numbers are HARD. As a teacher, I know students are comfortable working in the abstract when they can explain their math thinking within context and outside of a process of steps. Questions I ask students might include
- What is the question?
- What are the numbers in the problem?
- What do I need to do with the numbers?
- What is the answer?
- How can I confirm the answer?
CSA in Action: Word Problems
Word Problems are an easy way to gauge where students are with a specific skill. When looking at student work under a word problem, I’m able to easily see if they are using manipulatives (i.e. this is something that would need to be observed), drawing models or illustrations of what’s happening in the story, or using abstract numbers (or mental math strategies) to solve the problem. The one caveat to mental math strategies is that students MUST be able to answer the 5 questions above about the problem and their answer. If students can’t answer those questions, I know there could be (1) a gap in their concrete or semi-concrete experiences (i.e. have they been taught a procedure or math ‘trick’ for solving problems and do not truly understand what they are doing or being asked to do, or (2) there are comprehension problems that needs to be addressed. Below is an example of what CSA might look like within a word problem. Note – I am NOT asking for students to show all three methods on every word problem; rather, I can gauge where students are in the learning process based on how they interact and engage with the problem.
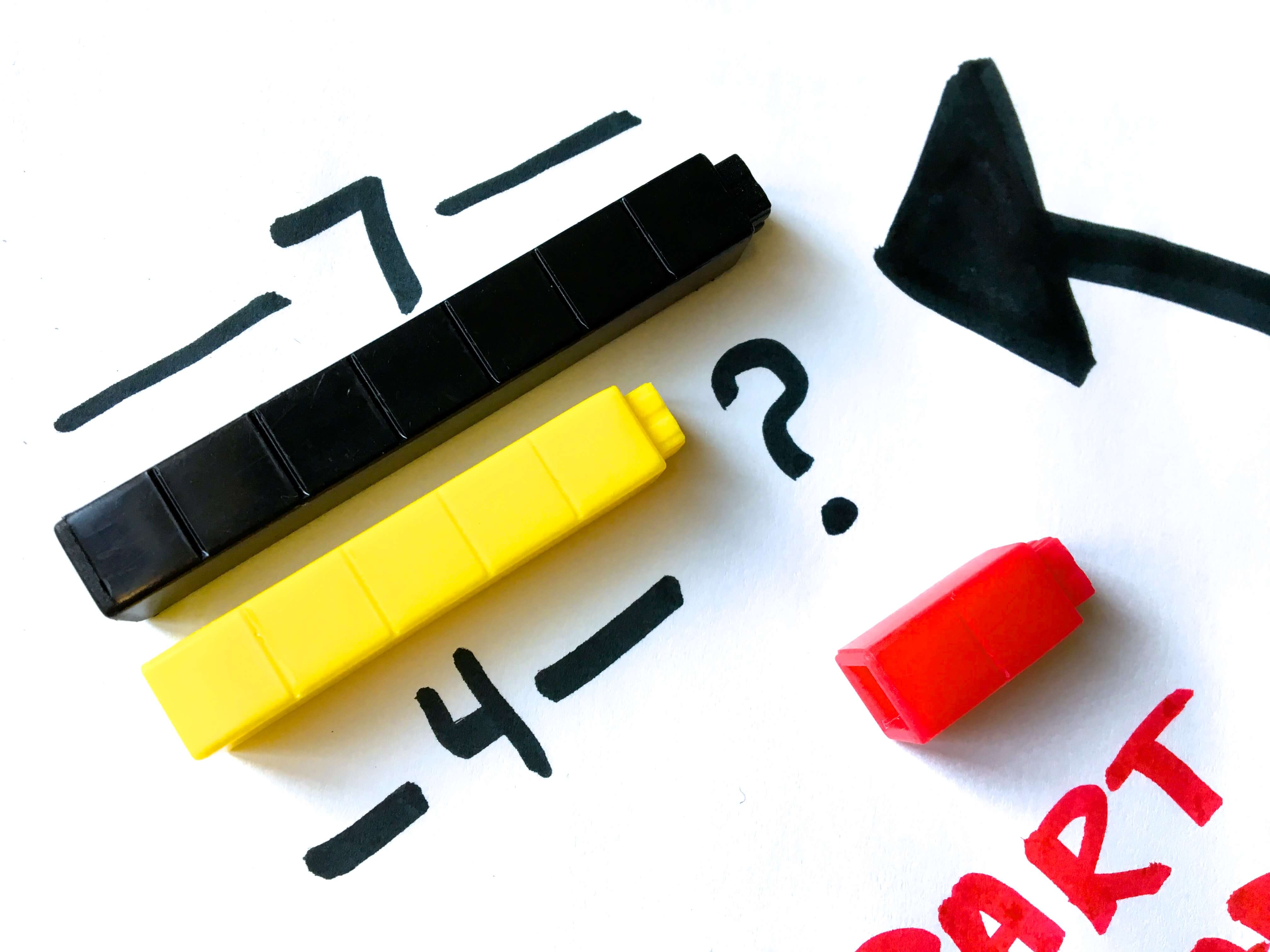
CSA in Action: Part, Part, Whole
Part, Part, Whole can be thought of in two distinct (but connected) ways. One – it can be thought of like comparing values. “I have a whole. It is next to a part. How much more is in the whole? How much less is in the part?” Two – part, part, whole can be thought of as a seamless transition between addition and subtraction. As teachers, we must create experiences that encourage strong concrete experiences with both of these ideas. When just beginning part, part, whole – we physically lay the part on top of the whole to find the missing part or difference.
As we start to understand this connection, we branch out to using cuisenaire rods. Now technically manipulatives, these AMAZING rods definitely have a learning curve. They are perfect for pulling out during PPW because it’s often a skill that students need TONS of practice with before they understand the connection between comparing values & addition/subtraction.
Then, branching into semi-concrete stage of learning we might draw a whole, crossing out the parts we already know to find what we still need.
Finally, we will make our way to those abstract ways to show part, part, whole (number bonds, part/part/whole boxes, etc.)
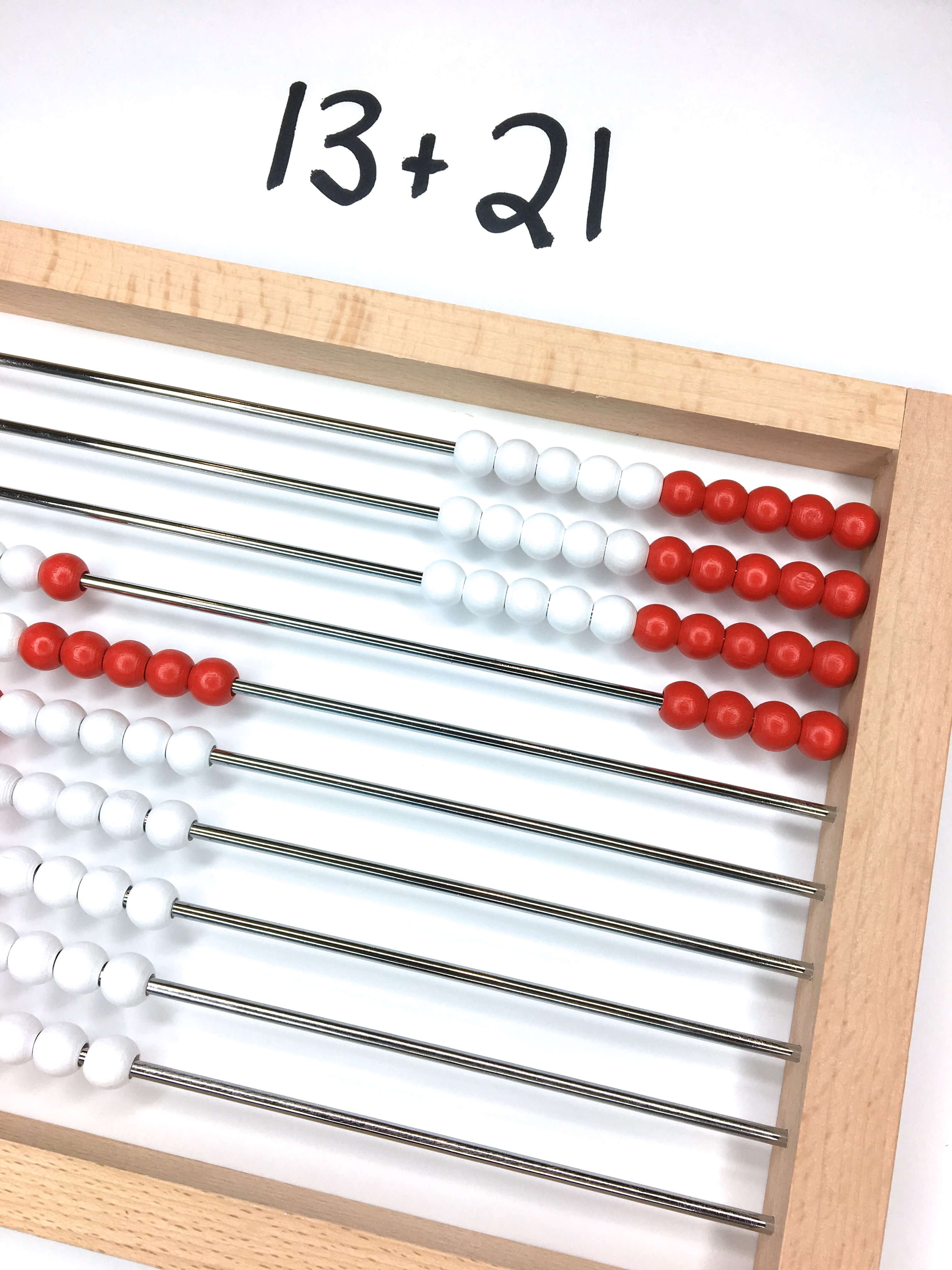
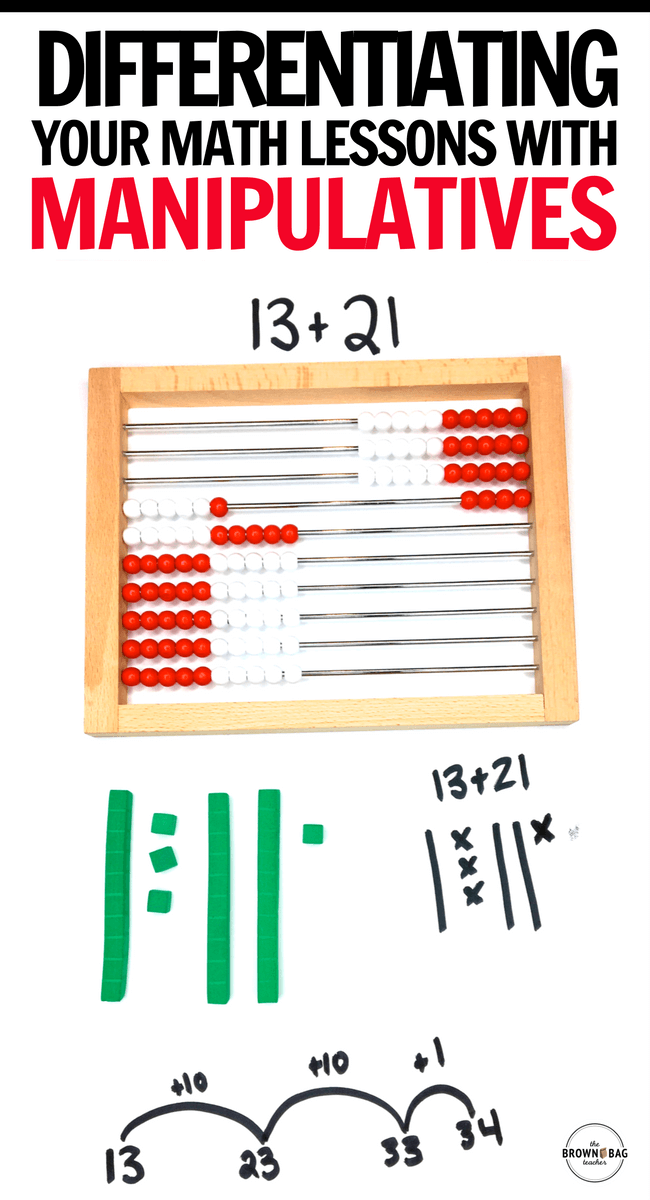
CSA in Action: Place Value
For place value, consider starting with an abacus rather than units/rods for the initially concrete learning. Students can individually manipulate beads, as well as, group beads. Then, branch into rods and units. Beginning with an abacus allows students to easily see how a group of 100 units interacts with one another, as well as, the idea of 10 beads = 1 row (1 rod) is incredibly concrete as they are joined on a medal row.
Then, in semi-concrete students might be using and drawing base 10 pieces. After students are able to add and subtract groups of 10 and understand that a number is made of tens and ones that we start using numbers. Even in this abstract state, students can still use manipulatives as a support but they might not choose to do so.
As instructional leaders in our classrooms, we have the power to observe student math behavior and intentionally push forward to strengthen a student’s math thinking. Working within CSA gives us a continuum to gauge student understanding and mastery of their learning. Knowing where students are along this continuum allows me to easily level and plan Guided Math lessons – pulling the just right manipulative, illustration, or number for students to work with. So friends, is CSA something you use in your classroom?
Get Free Teaching Resources!
Join me for weekly classroom updates and free resources that are just-right for your guided math classroom!





This is very interesting and has me thinking about how to better do small group math- thank you for sharing!
I have a question about the log. What are the two circles intended for?
Hey Pauline! I use those for recording Exit Slip scores. 🙂
We went to a training that used the same acronym and it really helped me to know how to plan for small groups and center to ensure differentiation! Thank you for showing more real world examples!
WOW! You give such clear explanations and beautiful examples. thanks for teaching this old dog new tricks.
Has anyone mentioned that the item you are calling an “abacus” is actually called a 100-Bead Rack or a Rekenrek?
I use them all the time but haven’t heard them called an abacus in a very long time. Christina Tondevold, aka the Recovering Traditionalist, is a blogger that teaches teachers how to use them as well. Lots of great information here, thank you.
They absolutely have multiple names! 🙂
You provide such lucid explanations, and the examples you present are lovely. Many thanks for showing this seasoned hound some fresh new tricks.
Differentiating math instruction can be challenging, but the CSA continuum (concrete, semi-concrete, abstract) offers a solution. Starting with concrete experiences, such as manipulatives, students develop a hands-on understanding. They then progress to semi-concrete representations like diagrams and charts, bridging the gap between concrete and abstract levels.
TUS Pendejadas | Series y TSomos una pagina que comparte series y novela donde buscamos la comodidad de las personas y evitamos descargas innecesarias y .
The CSA approach to math instruction is truly enlightening! I’ve always believed in the power of concrete experiences in early math learning, and it’s great to see a structured approach to it. I’m currently working on a programming research paper that explores the integration of technology in differentiated math instruction. I’ve been considering using https://writemyessays.com/research-paper.html to help refine my paper. Has anyone here tried their services for academic research? And how do you think technology can further enhance the CSA approach in the classroom?
Understanding this progression as a teacher allows us to assess where students are and intentionally scaffold them to develop their math thinking.
I appreciate you contributing your insights regarding this subject matter. It is crucial in the current era, and I appreciate the inclusion of the author’s or blogger’s name.
What do you use/do for your exit tickets in your small group instruction?